
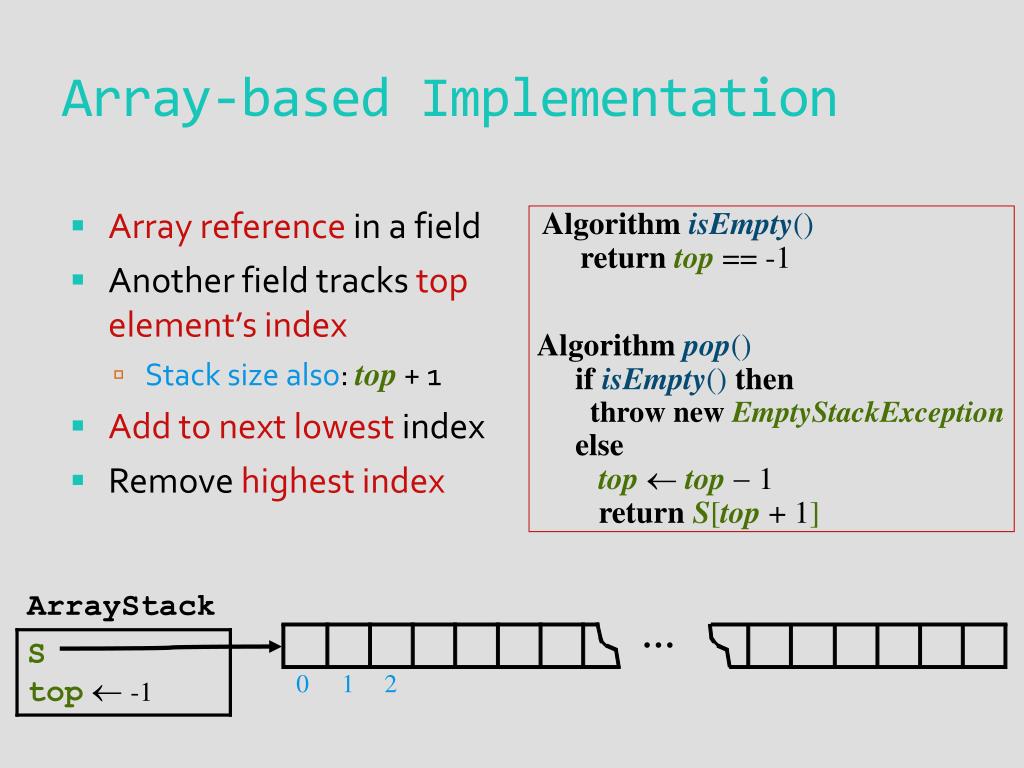

Similar(array,, )Ĭreate an uninitialized mutable array with the given element type and size, based upon the given source array. Reporting and analyzing crashes (segfaults).
#BASE ONE ARRAY CODE#

Talking to the compiler (the :meta mechanism).High-level Overview of the Native-Code Generation Process.Noteworthy Differences from other Languages.Mathematical Operations and Elementary Functions.", was found at position " & i & " in the array. The value you have entered in the input box. 'loop through the array and match each value with the _ StrMsg = "Your value, " & varUserNumber & _ 'message to show if the value doesn't found. If Not IsNumeric(varUserNumber) Then GoTo Loopback 'it's an IF statement that checks for the value that you _ ("Enter a number between 1 and 10 to search for:", _ 'it is an input box that asks you the number that you want to find. 'This part of the code adds 10 random numbers to _ That you need to search within the array. 'this section declares an array and variables _
#BASE ONE ARRAY HOW TO#
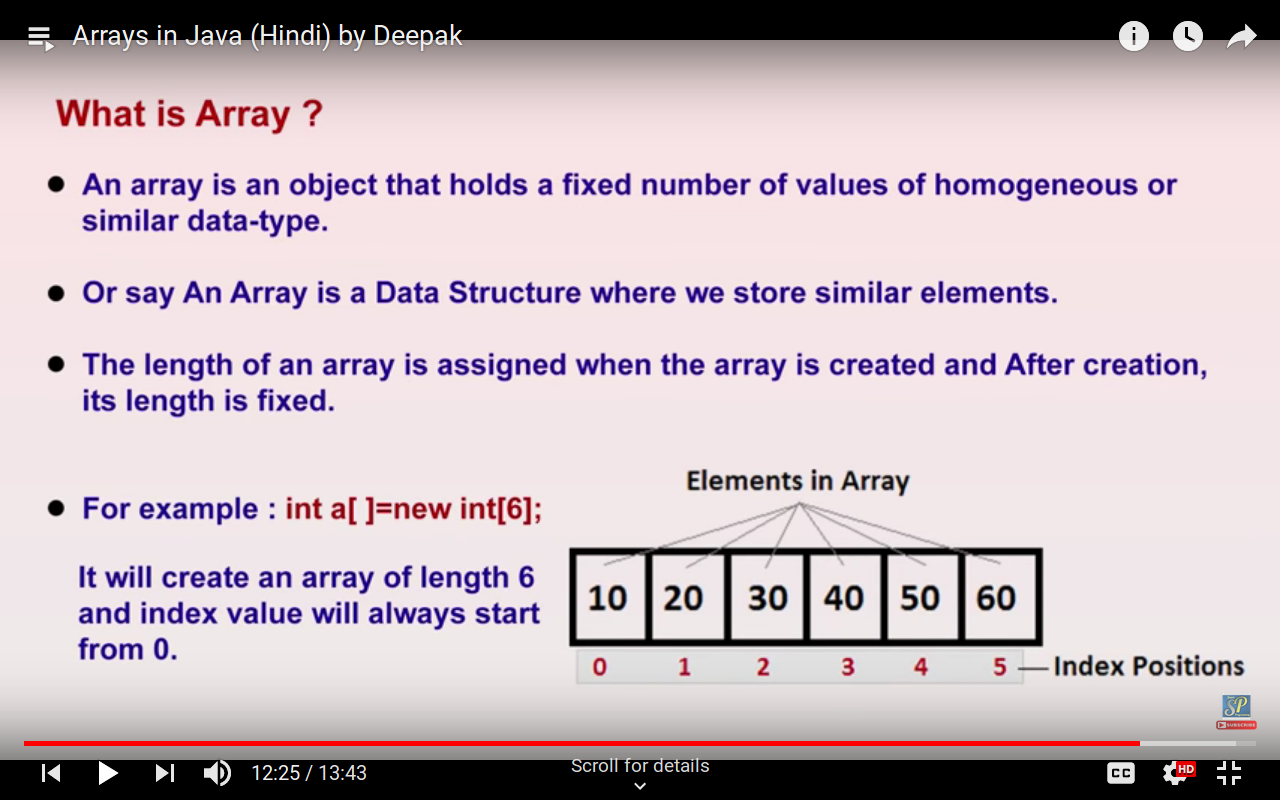
Now, look at the below code that can help you to understand how to search for a value in an array. In that case, you need to know the methods that you can use. When you store values in an array there could be a time when you need to search within an array. For example, if you want to return the 8th item in the area that we have created in the earlier example, the code would be: Returning Information from an ArrayĪs I mentioned earlier to get information from an array you can use the index number of the element to specify its position. So, it’s better to define a specific data type when you are declaring an array unless there is a need to use the variant data type. While declaring an array if you omit to specify the data type VBA will automatically use the variant data type, which causes slightly increased memory usage, and this increase in memory usage could slow the performance of the code. After that, you have 10 lines of code that define the elements of an array from 0 to 9.In the above code, first, you have the Dim statement that defines the one-dimensional array which can store up to 10 elements and has a string data type.In the end, to assign a value to an item in an array you need to use item’s index number to identify it and then assigning a value to it.After that, you need to define the number of items that you want to store in the array.If you do not have any data type specified VBA will assign appropriate data type. Next, you need to specify the data type for the array.First, use the keyword “Dim”, enter the name of the array, and type parentheses.Let’s say you want to declare an array that we have used in the above example. Unlike a normal variable, when you declare an array you need to use a pair of parentheses after the array’s name. How to Declare an Array in VBAĪs I mentioned above an array is the kind of variable, so you need to declare it using the keywords (Dim, Private, Public, and Static). But ahead in this guide, we will learn about multidimensional arrays as well. The array that we have used in the above example is a single-dimension array. So, if you want to use an element that is in the eighth position you need to refer to that element using its index number. In the above example, you have an array with ten elements (size of the array) and each element has a specific position (Index).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
